Come find out how to safely find, identify and eat chanterelle mushrooms, a gourmet summer delicacy!
Table of contents:
Feel free to jump right to the section you’re interested in or gobble up all the information provided:
1. Our introduction to chanterelle mushrooms
2. Chanterelle mushrooms of the Southeast United States
3. How to find chanterelles
4. How to identify chanterelle mushrooms and lookalikes
5. Harvesting, cleaning, storing, and eating tips
1. Our introduction to chanterelle mushrooms
About a decade ago, we were newbies to mushroom foraging. With good reason, we were hesitant to forage wild mushrooms since there are quite a few mushroom species that can kill you or make you very sick.
Thus, we did a bunch of reading and research about edible wild mushrooms in our area (Greenville, SC / Southeast US) before we even considered going mushroom foraging. Thankfully, we also have good friends who were experienced mushroom foragers, and they took us out for our first foray at some of their favorite spots.
It was a hot June day and rain had been plentiful during the weeks before the hunt (perfect weather conditions for chanterelles). As we drove down a dirt rode to the prime foraging spot in an old hardwood forest (perfect chanterelle habitat), our friends began excitedly shouting… “There’s one! Ooh, another one! They’re everywhere!”

A nice plate full of different types of chanterelle mushrooms commonly found in our area.
Along the moss-covered ditch next to the forest-shaded road, small red and slightly larger orange mushrooms were clearly visible from the car windows. This was our first encounter with chanterelle mushrooms in the wild.
Over the course of the next two hours, our group of merry foragers gathered about 30 pounds of chanterelles. The Tyrant and I were hooked!
Needless to say, our gourmet wild and home-cultivated mushroom addiction has only grown stronger over the decade since our first chanterelle hunt. Each summer since, we eagerly return to the woods to hunt chanterelles and other wild seasonal mushrooms.
2. Chanterelles of the Southeastern United States

Three general types of chanterelle mushrooms that we find in Upstate South Carolina in the Appalachian Mountains – orange chanterelles, black chanterelles, and red chanterelles. (See species names and descriptions below.)
“Chanterelles” are actually a very broad descriptor that may refer to a wide range of mushroom species in the genera Cantharellus and Craterellus, depending on what bioregion you live in. For instance, there are species of white chanterelle mushrooms on the west coast that we don’t have here on the east coast.
Where we live in the southeastern United States, there are three distinct color groups of mushrooms commonly called chanterelles that we regularly see and forage:
1. RED chanterelles – Cantharellus cinnabarinus
Red chanterelles are commonly called “cinnabars.” They’re absolutely gorgeous in color and shape, but they’re very small and thin-fleshed. The largest cinnabar mushroom might top out at 1.5″.
When we find a particularly abundant and large-sized patch of cinnabars, we’ll pick them, otherwise we tend not to mess with them since they’re so small.

Cinnabars! Aren’t they cute?
What do cinnabars taste like?
Cinnabars taste almost exactly like orange chanterelles: mild notes of apricot and almonds. There’s just not as much substance to them.
2. BLACK chanterelles – Craterellus fallax
Black chanterelles — which are not in the same genus as orange and red chanterelles — are also commonly called “black trumpets.” Black chanterelles are larger than cinnabars, but typically smaller than orange chanterelles. They are also very thin-fleshed.
Our east coast black trumpets/chanterelles look identical to west coast and European black trumpets, but are actually a distinct species.

Black trumpet chanterelles fruiting right next to an umbrella polypore. This was a VERY good foraging day!
What do black trumpet chanterelles taste like?
In our opinion, black trumpets might just be the most delicious mushroom in North America. They have a rich earthy complex flavor that is nearly comparable to truffles.
When we find big hauls of black trumpets, we dry and powder them, then cook them in olive oil to make black trumpet-infused dipping oil for our homemade bread. So dang good!
3. ORANGE chanterelles
“Orange” chanterelles may be a bit of misnomer since their color can range from pink to peach to yellow to orange, depending on the subspecies. Orange chanterelles are often lumped under the species name Cantharellus cibarius, but there are actually lots of different subspecies of orange-colored chanterelles with slightly different colors, shapes, and false gill patterns.
For example, in our area there’s pink/peach-colored Cantharellus velutinus, C. appalachiensis with maroon hues on the cap, smooth and orange C. lateritius, and others.

A beautiful orange chanterelle mushroom. Based on its smooth, shallowly wrinkled undersurface, this one is likely Cantharellus lateritius, although genetic analysis might reveal it to be another subspecies of chanterelle.
It’s likely that — just as with oak trees — there are hundreds of closely related yet genetically distinct chanterelle subspecies across North America. Not to worry, once you get the hang of ID’ing orange chanterelles, it becomes quite easy to know when you’ve got the real thing, despite these subtle differences!
What do orange chanterelles taste like?
Orange chanterelles are so popular for a good reason: they’re absolutely delicious when cooked. The flavor of orange chanterelles is subtle, offering notes of apricots, almonds, and pleasant umami-earthiness.
3. How to find chanterelle mushrooms

A beautiful flush of chanterelle mushrooms growing in a forest in Upstate South Carolina in early July.
What states can you find chanterelles in?
In addition to their amazing flavor, another nice thing about chanterelle mushrooms is they are widely distributed across the United States. In fact, you can find chanterelles in 49 out of 50 US states! (Sorry, Hawaii.)
Where do chanterelles grow?
You can NOT grow chanterelles; you can only forage them. Coincidentally, this is why chanterelles are so expensive when you buy them!
Chanterelles are mycorrhizal, meaning they form symbiotic relationships with tree roots of specific trees. They feed their host trees and their host trees feed them — interspecific mutualism.

Shaded forest floor with a giant beech tree – the perfect spot to find chanterelles!
That’s why you’ll only find chanterelles growing in mature forests. If you see something you think is a chanterelle growing in the middle of a field or meadow, it’s highly unlikely that it’s a chanterelle.

A closer look at the forest floor from the image above. See those beautiful chanterelle mushrooms popping?
In our area, chanterelles grow primarily around the following hardwood trees: beech, oak, and maple. However, in other areas of the country, chanterelles (and various subspecies of chanterelles) can even be found associating with evergreens.
When we forage chanterelles with our family in the South Carolina lowcountry, we’ve even found chanterelles growing in pine forests!
When do chanterelles grow?
Chanterelles are a heat-loving summer mushroom, but they can also be found into fall in warmer areas. The earliest we’ve ever found chanterelles in Greenville, SC is the first week of June. The latest we’ve ever found them is early October.
How long after rain do chanterelles grow?
A heavy summer rain will trigger the underground chanterelle colony to begin fruiting almost immediately, but the mushrooms take a while to develop and won’t be visible for many days after. For instance, we just came out of a severe May drought (zero rain) followed by about 6″ of rain in early June. 10 days after the heavy rains and the first chanterelles of the season are about 1″ tall mushrooms — not yet large enough to harvest.
Chanterelles LOVE lots of rain. If you’re in the middle of a summer drought, you won’t find chanterelles. The best case scenario for an amazing chanterelle mushroom season is regular deep-drenching summer thunderstorms.

MOAC (Mother of All Chanterelles), aka the largest chanterelle we’ve ever seen.
4. How to identify chanterelle mushrooms and lookalikes
As mentioned above, there are red, black, and orange chanterelle species. They all grow in the same conditions: in older forests during wet summers.
The most commonly foraged and sold chanterelles are orange chanterelles due to their larger size (it doesn’t take nearly as long or as many mushrooms to get a pound of orange chanterelles relative to black and red chanterelles).
In addition to season and location characteristics, here are key identifying features of orange chanterelles:
- Color range: Orange, peach, yellow, pink
- Shape: Vase-like
- Gill structure: The underside of chanterelles contains rows of false gills (they don’t produce spores except under the cap). The false gills fork, unlike true gills that look like single, individual blades. The false gills terminated at the stem, which is smooth. In some chanterelles, these false gills are much more pronounced than in others.
- Spore print: Light yellow to white
- Growth habit: Orange chanterelles generally grow as individual mushrooms, but sometimes can be found in small clusters.
- Smell: Orange chanterelles smell sweet, fruity and pleasant (slight apricot smell).

The underside of red chanterelles (cinnabars) shows you the forked false gill structure referenced above.
Do chanterelles have poisonous and non-poisonous lookalikes?
Yes! Depending on where you live, there are likely to be a few mushroom species that look somewhat like chanterelles. However, once you have some experience, distinguishing between real chanterelles and their lookalikes becomes very easy.

Hedgehog mushroom (left) our favorite chanterelle lookalike, next to actual chanterelles (right). Hedgehogs are another choice edible mushroom. Be warned that some chanterelle lookalikes are poisonous!
Remember to always comply with our rule #1 of foraging: Never eat anything you’re not 100% certain you’ve correctly ID’d AND you’re not 100% certain is edible. If you’re a new or inexperienced forager, you should have an experienced forager with you to help you correctly ID chanterelles until you get the hang of it.
Here are some chanterelle lookalikes in our area:
1. Jack-o-lantern mushrooms(Omphalotus illudens) – These are poisonous! Jack-o-lantern mushrooms have a bright orange color and their gills actually glow green at night. Individual jack-o-lantern mushrooms look somewhat similar to chanterelles, but their growth habit is different.
- Distinguishing characteristics: jack-o-lanterns grow in clusters and decompose dead trees and roots. You’ll often see them growing on decomposing stumps, whereas chanterelles don’t grow on decomposing wood.
2. False chanterelles (Hygrophoropsis aurantiaca) – Yes, as the name implies, false chanterelles look pretty similar to the real thing. There isn’t a consensus on whether false chanterelles are edible or poisonous. Some people eat them without incident, and others report having an upset stomach after consumption. Our recommendation: stay away, especially since they’re not supposed to taste great.
- Distinguishing characteristics: False chanterelles have true gills and are a deeper orange color than real chanterelles.
3. Hedgehog mushrooms (Hydnum spp) – If you find this chanterelle lookalike, you’ve hit the jackpot! Hedgehog mushrooms aren’t only edible, they’re delicious. We actually like them as much as orange chanterelles. Unfortunately, they seem to be far more rare in our area than chanterelles.

A large hedgehog mushroom, possibly Hydnum repandum.
- Distinguishing characteristics: The underside of hedgehog mushrooms is covered with tiny white teeth/spines where the spores are released (versus the false gills of chanterelles).
Related: Read our article How to find, ID, and eat hedgehog mushrooms.
5. Harvesting, cleaning, storing, and cooking tips
Once you know how to ID chanterelles, it’s time to harvest them. Our rule #11 of foraging: harvest sustainably. With that rule in mind, here are five chanterelle harvesting tips:
1. Pull then cut and clean
Common wisdom we learned when starting to forage mushrooms years back was that you should cut chanterelle mushrooms at the base of their stems rather than pulling them out of the ground. This would supposedly minimize damage to the underground organism.
However, multi-year research has shown that whether you pull or cut chanterelles while harvesting “… has little significant influence on either chanterelle abundance or biomass, although it appears that there is a trend towards increased abundance and biomass in the pulled plots.”
In other words, it makes very little difference to the health of the organism whether you pull or cut the fruiting bodies during harvesting. Our recommendation? Pull chanterelle mushrooms from the ground when harvesting, but cut and remove the dirt-covered bases BEFORE you put them in your harvest basked in order to reduce the amount of time you have to clean your mushrooms when you get home.
2. Don’t bother picking dirt-covered chanterelles.
Only pick clean chanterelles (ideally growing out of leaf litter), leaving behind any that are coated in dirt, sand, or grit. It’s not worth the aggravation of cleaning extremely dirty chanterelles and chewing on grit during a meal can ruin the experience.
Plus, leaving some mushrooms behind helps them continue to spore out and further colonize the area.
3. Harvest larger chanterelles, not immature “buttons.”
Only harvest larger, more mature chanterelle mushrooms rather than very young ones, aka buttons. This helps ensure that they’ve had a chance to produce plenty of spores. Relative to other mushrooms, chanterelles are slow-growing and release their spores over a longer time period.
4. Be a spore spreader.
Use a breathable basket or linen bag when harvesting chanterelles, NOT plastic or other non-breathable collection bins. This allows the mushrooms you pick to spore out as you walk, helping to seed the forest floor with new chanterelle colonies.

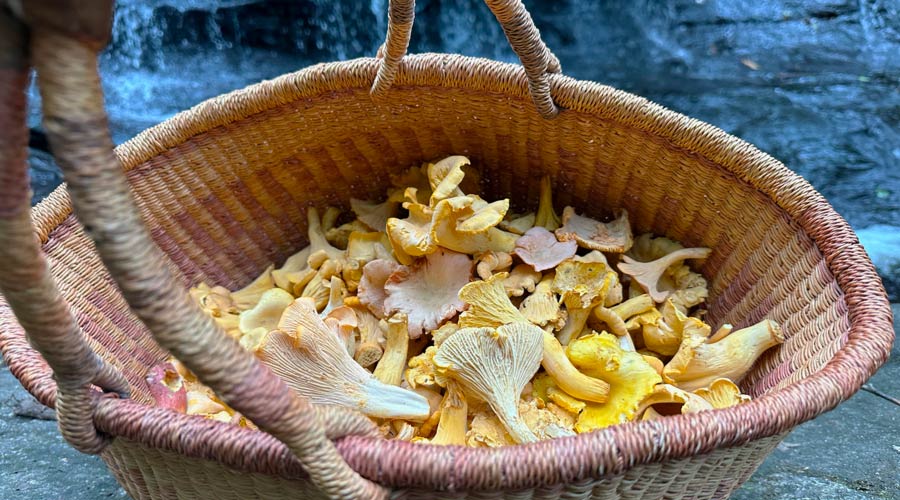
Sure, this harvest basket looks cool, but that’s not why we use it. It keeps our foraged mushrooms from getting smushed while we hike and it also helps spread the spores of the mushrooms within far and wide.
5. Only harvest what you’ll eat or dehydrate.
Only harvest what you’ll reasonably use immediately or have time/ability to prep for long-term storage. There’s no reason to harvest mushrooms only to let them rot in your fridge.
When we have an abundance, we like to dehydrate then blend them into a powder. This is a great way to turn a giant heap of mushrooms into something you can store in a jar and use throughout the year. And dried or powdered chanterelles taste great.

A gorgeous pile of gourmet summer forest mushrooms, including different types of chanterelle mushrooms.
Yes, you can rinse chanterelles – and you should.
If you’re discerning about which chanterelles you harvest, there should be very little dirt or grime on them. However, we’d still recommend starting meal prep with completely clean, dirt and grit-free chanterelles.
We use a drinking-safe garden hose with a sprayer set to the mist setting to clean chanterelles in our yard. We place them on a metal table with a lattice top, spray each mushroom, then set it on a towel to dry for about 15 minutes before storing them in bags in our fridge.
Does rinsing chanterelles diminish their flavor? Not that we can discern.
How long do chanterelles last? How do you use or store chanterelles?
Once you harvest chanterelles, the clock starts ticking… You’ll want to get them cleaned, bagged, and refrigerated as soon as possible.
- Left in an unrefrigerated pile in your harvesting basket, chanterelles will start to go bad within 48 hours — or less if they’re wet.
- Refrigerated chanterelles in good condition can last for about a week in a ziplock bag.
- Dehydrated chanterelles stored in an airtight jar can last for years.
- Frozen chanterelles can last for 1+ years, but we prefer dehydration as a long-term storage method.
Chanterelle cooking tips
Always cook chanterelles and other mushrooms before eating them! (Mushroom expert Paul Stamets explains why here.)
Chanterelles are a subtle flavor so use them accordingly. Don’t use them in highly flavorful sauces such as curries or tomato sauces, or you won’t taste them. The point is to accentuate the flavor of the chanterelles, not drown them!
A good place to start with chanterelles in your kitchen is as follows:
- in cream and/or white wine sauces served with organic whole wheat pasta or orzo with parmesan cheese (see recipe: Orzo with chanterelle mushrooms and Common milkweed)
- with mild meats like chicken, or
- sautéed in butter or olive oil with shallots and garlic.
We hope this article was helpful and gets you looking at a forest floor in a whole new light! The world around you is full of wild gourmet food, but ALWAYS forage safely and never put you or your loved ones at risk by eating foods you haven’t properly identified.

KIGI,

Other articles you might enjoy:
- Recipe: Orzo with chanterelle mushrooms and Common milkweed
- 6 gourmet and medicinal mushrooms you can easily grow in your garden
- How to find, identify, grow, and cook chicken of the woods mushrooms
- How to find morel mushrooms in the southeast US
- How to grow shiitake mushrooms
- How to find and prepare maitake mushrooms
- A delicious indigo milkcap recipe
Like what you're seeing here? Please be sure to subscribe to Tyrant Farms so we can let you know about new articles you'll love.

2 Comments
Jason H
June 25, 2023 at 10:02 amThanks for this post! I have been noticing chanterelle-like mushrooms but internet searches where making me apprehensive. It’s nice to see something from a regional forager and, thanks to your post, I know believe what I am finding are Red Chanterelles(which I didn’t know existed until just now!)
Thanks again!
Aaron von Frank
June 26, 2023 at 6:59 amHappy to help in your chanterelle exploration! Cinnabars/red chanterelles might be smaller than their orange cousins, but they’re a fine edible mushroom. Since this is a new one for you, just make sure you have the ID right prior to cooking and eating.